In his introduction to this issue, Dr. Sami Nizam shows how remote anchorage is becoming an increasingly important tool in implant dentistry.

Remote anchorage of dental implants is an innovative concept in implant dentistry designed to improve the stability, retention, and overall effectiveness of implant-supported restorations. Traditionally, dental implants are anchored directly into the alveolus to replace missing teeth, with the goal of providing strong, functional, and esthetic replacements. However, in cases where the bone density is insufficient or the anatomical structures are compromised, remote anchorage can offer an alternative solution.
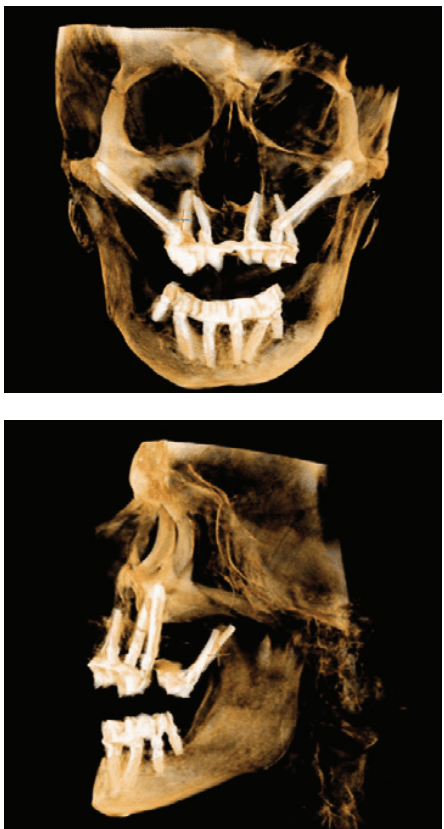
The term remote anchorage refers to the use of alternative support structures outside of the typical alveolar bone housing to stabilize dental implants. Examples include the pterygoid region of the maxilla, the zygoma, and the lateral nasal wall/inferior turbinate, nasopalatine duct, and anterior nasal spine. These anchorage points are typically located outside the immediate area of traditional implant sites, providing greater flexibility in cases where the direct implant site cannot provide enough support. These techniques circumvent challenges related to bone volume and quality, making it an effective solution for patients with insufficient bone, such as those with severe periodontal disease, extensive bone loss, sinus pneumatization, or after tooth extraction.
Benefits of remote anchorage
- Reduced need for bone grafting: One of the most significant advantages of remote anchorage is that it reduces the need for invasive bone-grafting procedures. By using existing bone at remote sites, clinicians can avoid the additional pain, surgeries, and cost of bone augmentation, which carries with it lower success rates.
- Improved implant stability: In cases where the local bone is compromised or soft, remote anchorage can offer enhanced stability by shifting the load and stress to more stable structures and allowing immediate loading.
- Expanding treatment options: Remote anchorage broadens the possibilities for patients who would otherwise be considered unsuitable candidates for dental implants due to insufficient bone or complex anatomical challenges.
- Reduced treatment time: With appropriate remote anchorage, patients may avoid the lengthy healing times associated with bone grafting or sinus lift procedures, reducing the overall duration of treatment.
- Higher success rates: As we are typically engaging native cortical bone sites, higher success rates are achievable.
- Elimination of cantilevers: The use of pterygoids and posteriorly placed zygomas can eliminate cantilevers and allow restoration back to second molar.
Remote anchorage of dental implants provides a promising solution for patients with insufficient bone or challenging anatomical conditions and allows immediate function. By utilizing adjacent structures or extraoral support systems, this technique can enhance implant stability, reduce the need for bone grafting, and offer greater flexibility in complex cases. However, careful planning and precise execution are crucial to ensuring the long-term success and stability of the restoration. As research and technology advance, remote anchorage is likely to become an increasingly important tool in the field of implant dentistry.
Stay Relevant With Implant Practice US
Join our email list for CE courses and webinars, articles and mores



